Describe in Words How to Calculate an Empirical Formula
The ratio of atoms is the same as the ratio of moles. The simplest ratio of H.

Empirical Formula Definition Steps Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
In chemistry the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest positive integer ratio of atoms present in a compound.

. N is the total number of trials. The complicated formula above breaks down in the following way. The empirical formula of the compound is Fe 2 O 3.
Assume a 100 g sample. Determine the mean of the data set which is the total of the data set divided by the quantity of numbers. Multiply each of the moles by the smallest whole number that will convert each into a whole number.
Remember that if you calculate a number that is x09 round to the nearest whole number. By dividing the lowest number alter the numbers to whole numbers. Then input those values into the formulas below to derive the ranges.
To make the calculation easier assume the total mass of a sample is 100 grams so you can work with simple percentages. N --- 2631 mol 2631 mol 1 O --- 3947 mol 2631 15 Multiply by 2 to N 2 and O 3 N 2 O 3 is the empirical formula. Formula to calculate empirical formula.
Divide both moles by the smallest of the results. Find out the molecular formula of that compound. To work out the empirical formula you need the mass of.
Empirical Probability Formula fn. Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles. 134 Triple only.
Because the original percent composition data is typically experimental expect to see a bit of error in the numbers. Empirical formula is same as molecular mass as n1 this means molecular formula is. However its usual to use the smallest whole number ratio of atoms.
FeO 2 115 23. Write down the empirical formula. The formula could be articulated as H1110O5549.
Let us understand the empirical probability formula using solved examples. C 3 H 4 O 3. For example the empirical formula of a hydrocarbon is CH 2 and its M r is 42.
Molecular formula 6 x CH 2 O molecular formula C 1 x 6 H 2 x 6 O 1 x 6 molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. Add up the atomic masses of the atoms in the empirical formula. 204g of H 1008gm-1 2024 moles of H 3 Then pick the smallest answer in moles from the previous step and divide all the answers by that.
Empirical probability can be defined as the estimator of probability based on experiences and observations. 133 calculate empirical and molecular formulae from experimental data. For example 203 is probably within experimental error of 2 299 is probably 3 and so on.
110 describe these experimental techniques for the separation of mixtures. H 1110 5549 2000. Use the molar mass you get.
The empirical formula of a compound is COCl 2 and its molecular mass is 9000u. Simple distillation fractional distillation filtration crystallisation paper chromatography. Determine the masses of each component in the compound.
Definition of Empirical Probability. Calculate the molecular weight of the empirical formula the molecular weight of C 12011 gmol and H 1008 gmol 5 120111 gmol 11 1008 gmol C 5 H 11 60055 gmol 11008 gmol 71143 gmol per C 5 H 11. Since the moles of O is still not a whole number both moles can be multiplied by 2 while rounding to a whole number.
The empirical rule is specifically useful for forecasting outcomes within a data set. Mass of magnesium oxide mass of Mg mass of O. Determine the number of moles by dividing the grams by the atomic mass.
0493 g 0297 g mass of O. Percentage of data in the range. Where f is the number of times an event occurs.
The formula is given below. 132 know what is meant by the terms empirical formula and molecular formula. First the standard deviation must be calculated.
The non-whole number empirical formula of the compound is Fe 1 O 15. It takes six empirical formula units to make the compound so multiply each number in the empirical formula by 6. COCl 2 C O 2Cl 12 16 2355 99 u.
Mass of Mg 0297 g. Calculate the mass of the magnesium oxide by subtracting the mass of the empty crucible. 4 Simplify mole ratio to get empirical formula.
Empirical Rule Formula 68 95 99 Rule To calculate the data ranges associated with the empirical rule percentages of 68 95 and 997 start by calculating the sample mean x and standard deviation s. The empirical formula for our example is. To do this all you have to do is write the letters of each component in this case C for carbon H for hydrogen and O for oxygen with their whole number counter parts as subscripts.
In most cases this ratio needs to be multiplied by a number to give a series of whole number ratio. But as two fractions are present in the series that are very close to whole numbers the ratio can be rounded off ie CHO 461. Since the moles of O is still not a whole number both moles can be multiplied by 2 while rounding to a whole number.
5 Compare molecular mass to empirical unit mass to get number of empirical units per molecule and thus molecular formula. The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. N 2 O 3 weighs 760 1520 760 2 N 2 O 3 times 2 N 4 O 6.
O 5549 5549 1000. How to Determine Empirical Formula Begin with the number of grams of each element which you usually find in an experiment or have given in a problem. Think about your result.
So our job is to calculate the molar ratio of Mg to O. 10203 moles of S 10203. The empirical formula is thus N 2 O.

Empirical Formula Definition Get Education

Empirical Formula Calculator How To Find Empirical Formula Of A Compound
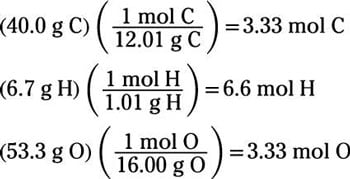
How To Calculate The Empirical Formula Of A Compound Dummies
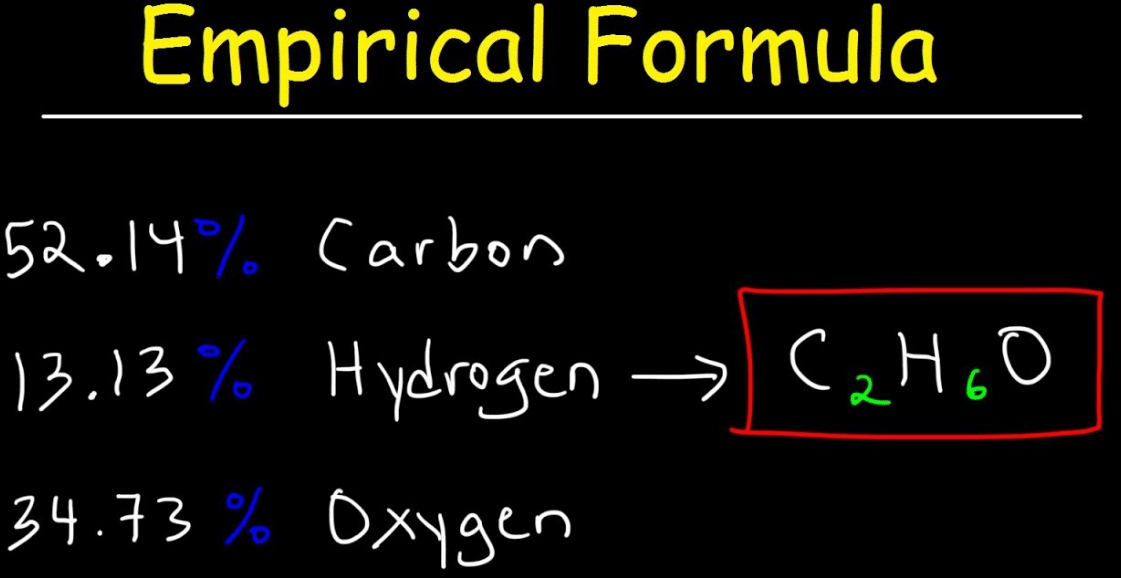
No comments for "Describe in Words How to Calculate an Empirical Formula"
Post a Comment